WGU Pathophysiology
Total Questions : 52
Showing 25 questions, Sign in for more1. This pathogen organism can be difficult to treat due to its resistance to treatment and can progress into blood, bone, lung, or skin infections that may be life-threatening. Which type of infectious disease is described?
Explanation
MRSA stands for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, a type of bacteria that is resistant to many antibiotics and can cause serious infections in various parts of the body. MRSA can spread through direct contact with infected people or contaminated objects and can be difficult to treat due to its resistance to treatment. MRSA can progress into blood, bone, lung, or skin infections that may be life-threatening if not treated promptly and appropriately.
Older adults generally mount lower immune responses to vaccines.
Which age-related change is likely to contribute to these lower immune responses?
Explanation
Naïve T cells are a type of white blood cell that has not encountered a specific antigen before and are ready to respond to new infections. As people age, the number of naïve T cells decreases due to the shrinking of the thymus gland, which produces and matures T cells. This reduces the ability of the immune system to recognize and fight new pathogens and lowers the effectiveness of vaccines.
What is a clinical manifestation of dehydration?
Explanation
Oliguria is a condition where the urine output is less than normal, usually less than 500 mL per day in adults. Oliguria can be a sign of dehydration, which occurs when the body loses more water than it takes in. Dehydration can cause various symptoms such as thirst, dry mouth, headache, dizziness, fatigue, and confusion.
Dehydration can also affect kidney function and lead to electrolyte imbalances and acid-base disorders.
A patient experiences significant blood loss after surgery, which raises the osmolarity of the bloodstream. Which fluid changes are expected to occur within this patient's body as a result?
Explanation
Osmolarity is a measure of the concentration of solutes in a solution. When the osmolarity of the bloodstream increases due to blood loss, water will move from areas of lower osmolarity to areas of higher osmolarity by osmosis. This means that water will move from the extracellular fluid (the fluid outside the cells) to the intracellular fluid (the fluid inside the cells) to balance the osmotic pressure. As a result, the extracellular fluid volume will decrease and the intracellular fluid volume will increase, causing the cells to expand.
Which hormone is secreted in response to low levels of calcium in the bloodstream?
Explanation
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is a hormone produced by the parathyroid glands, which are located behind the thyroid gland in the neck. PTH regulates the calcium levels in the blood by stimulating the release of calcium from the bones, increasing the absorption of calcium from the intestines, and decreasing the excretion of calcium from the kidneys. When the calcium levels in the blood are low, PTH is secreted to raise them back to normal.
Older adults generally mount lower immune responses to vaccines. Which age-related change is likely to contribute to these lower immune responses?
Explanation
Naïve T cells are a type of white blood cell that has not encountered a specific antigen before and are ready to respond to new infections. As people age, the number of naïve T cells decreases due to the shrinking of the thymus gland, which produces and matures T cells. This reduces the ability of the immune system to recognize and fight new pathogens and lowers the effectiveness of vaccines.
Which infectious disease interferes with the human immune system, leaving the body open to opportunistic infections?
Explanation
HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus, a virus that infects and destroys CD4+ T cells, which are a type of white blood cell that coordinates the immune response against foreign invaders. HIV can cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), which is a condition where the immune system becomes severely weakened and unable to fight off common infections and cancers. HIV can be transmitted through sexual contact, blood transfusion, needle sharing, or mother-to-child transmission.
How does hypoventilation affect the blood's pH?
Explanation
More H and HCO3 form, decreasing the blood's pH.
Rationale: Hypoventilation is a condition where the breathing rate is too slow or shallow, resulting in insufficient removal of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the body. CO2 reacts with water (H2O) to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), which can dissociate into hydrogen ions (H+) and bicarbonate ions (HCO3-). Therefore, when CO2 accumulates in the blood due to hypoventilation, more H2CO3 is formed, which lowers the blood's pH by increasing the concentration of H+ and HCO3-.
An adult patient presents with a complaint of a cough that has lasted for two weeks. The patient has a rapid, shallow respiratory rate of 34 breaths per minute. Auscultation of the lungs reveals bilateral rhonchi in the upper lobes and diminished breath sounds in the bilateral lower lobes. The patient is diagnosed with bilateral pneumonia and respiratory alkalosis. What is the expected arterial blood gas laboratory value for this patient?
Explanation
Respiratory alkalosis is a condition where the blood's pH is elevated due to excessive removal of CO2 from the body. This can occur when the breathing rate is too fast or deep, such as in response to hypoxia, anxiety, fever, or lung disease. When CO2 is removed from the blood, less H2CO3 is formed, which raises the blood's pH by decreasing the concentration of H+ and HCO3- . A normal blood pH is between 7.35 and 7.45, and a normal partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide (PaCO2) is between 35- and 45 mm Hg. Therefore, a patient with respiratory alkalosis would have a higher-than-normal pH and a lower-than-normal PaCO2.
If a child has one parent with Marfan syndrome, what is the likelihood that the child will have Marfan syndrome?
Explanation
Marfan syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue, causing problems with the heart, blood vessels, eyes, bones, and joints. It is caused by a mutation in the FBN1 gene, which encodes for a protein called fibrillin-1. Marfan syndrome follows an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance, which means that only one copy of the mutated gene is needed to cause the disorder. A person with Marfan syndrome has a 50% chance of passing on the mutated gene to each child, regardless of the gender of the parent or the child.
What is an immediate bodily response to acidosis?
Explanation
Acidosis is a condition where the blood's pH is lowered due to an excess of H+ in the body. This can occur due to metabolic causes, such as diabetes, kidney failure, ingestion of toxins, or respiratory causes, such as hypoventilation or lung disease. The body has several mechanisms to compensate for acidosis and restore the normal pH balance. One of them is to increase the rate and depth of breathing, which helps to remove CO2 from the body and reduce the formation of H2CO3.
Which respiratory finding is expected in an attempt to compensate for metabolic acidosis?
Explanation
Metabolic acidosis is a condition where the blood's pH is lowered due to an excess of non-volatile acids in the body, such as lactic acid, ketoacids, or ingested acids. This can occur due to diabetes, kidney failure, diarrhea, or ingestion of toxins.
The body has several mechanisms to compensate for metabolic acidosis and restore the normal pH balance. One of them is to hyperventilate, which helps to remove CO2 from the body and reduce the formation of H2CO3.
A patient presents at a clinic with a partial-thickness burn on the left arm. The skin appears red and swollen. The patient reports the burn is very painful. What is an additional symptom of a patient with this type of burn?
Explanation
Partial-thickness burns are also known as second-degree burns. They involve damage to both the epidermis (the outer layer of skin) and part of the dermis (the inner layer of skin). They cause redness, swelling, pain, and blisters. Blisters are fluid-filled sacs that form as a result of damage to the skin cells and blood vessels.
They help to protect the underlying tissues from infection and further injury.
Which musculoskeletal disorder is caused by the overextension of muscles or tendons, causing the tearing of small vessels and nerve irritation?
Explanation
A strain is an injury to a muscle or a tendon that occurs when it is stretched or torn beyond its normal range of motion. Strains can result from overextension of muscles or tendons, such as lifting a heavy object, twisting or bending awkwardly, or performing repetitive motions. Strains can cause bleeding and swelling in the affected area, as well as pain and reduced function.
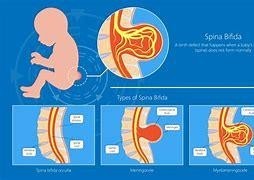
A nurse is counseling a woman about prenatal vitamins and focuses on the need for folic acid intake. Which disorder is a potential consequence of inadequate folic acid intake?
Explanation
Spina bifida is a birth defect that occurs when the neural tube, which forms the brain and spinal cord, does not close properly during early fetal development. This can result in an opening in the spine that exposes the spinal cord and nerves, leading to various complications such as paralysis, bladder and bowel problems, hydrocephalus, and learning difficulties. Folic acid is a B vitamin that is essential for the formation of the neural tube and other organs in the embryo. Inadequate folic acid intake before and during pregnancy can increase the risk of spina bifida and other neural tube defects.
Which disease can vitamin B12 deficiency be attributed to?
Explanation
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin that is involved in the production of red blood cells, DNA synthesis, and nerve function. Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause anemia, neurological problems, and cognitive impairment. Vitamin B12 deficiency can be attributed to alcoholism because alcohol interferes with the absorption and metabolism of vitamin B12 in the stomach and liver. Alcohol also damages the lining of the intestines, where vitamin B12 is absorbed from food sources.
Which complication of musculoskeletal trauma causes the accumulation of nephrotoxic myoglobin?
Explanation
Rhabdomyolysis is a condition that occurs when skeletal muscle tissue breaks down rapidly due to injury, infection, drug toxicity, or other causes. The breakdown of muscle releases myoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen in muscle cells, into the bloodstream. Myoglobin can damage the kidneys by clogging the renal tubules and causing acute kidney injury. Rhabdomyolysis can also cause electrolyte imbalances, muscle weakness, and compartment syndrome.
A patient was involved in a fight and was hit in the head with a chair. The emergency room physician noted the following signs and symptoms:
A patient appears confused and does not remember being in a fight: the patient was brought in by a friend. The patient is having problems concentrating, dizziness, and flat affect. Which condition is indicated by the physician's findings?
Explanation
A cerebral concussion is a mild traumatic brain injury that occurs when a blow to the head causes the brain to move rapidly inside the skull, resulting in temporary changes in brain function. A concussion can cause confusion, memory loss, impaired concentration, dizziness, headache, nausea, blurred vision, and mood changes. Most concussions resolve within a few days or weeks with rest and monitoring.
19. PET scan results indicate a tangled mass of nonfunctioning neurons replaced by senile plaques. Progress notes indicate deterioration of judgment, emotional detachment, and sleep disturbance.
The etiology is noted to be a genetic mutation. Which condition is reflected in this patient's record?
Explanation
Alzheimer disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects memory, cognition, behavior, and daily functioning. Alzheimer disease is characterized by the accumulation of amyloid-beta plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain, which impair the communication and survival of neurons. Alzheimer disease is influenced by genetic and environmental factors, and some rare forms of the disease are caused by mutations in specific genes.
A patient reports fatigue, shortness of breath, and vomiting. The patient was given medication for crushing chest pain that radiated to the neck and jaw. The patient's blood test showed elevated cardiac enzyme levels Which condition is described?
Explanation
This condition occurs when the blood supply to a part of the heart muscle is blocked, causing tissue damage or death. The symptoms of fatigue, shortness of breath, vomiting, chest pain, and elevated cardiac enzymes are all indicative of a myocardial infarction.
A patient's record has a transient ischemic attack (TIA) noted. What are the two symptoms of this condition?
Choose 2 answers
Explanation
Memory impairment. A TIA is a temporary interruption of blood flow to a part of the brain, causing neurological deficits that usually resolve within 24 hours. The symptoms of a TIA may include difficulty speaking, understanding, reading, or writing; confusion; memory loss; weakness or numbness on one side of the body; vision problems; or dizziness.
A patient has sharp, sudden chest pain and difficulty breathing. The physical exam reveals clammy skin and low blood pressure. The diagnostic procedure reveals inflammation in the saclike membrane of the heart muscle and a buildup of fluid. Which disorder is described?
Explanation
This condition is an inflammation of the pericardium, which is the thin layer of tissue that surrounds and protects the heart. The inflammation can cause fluid to accumulate in the pericardial space, which can compress the heart and impair its function. The symptoms of pericarditis may include chest pain that worsens with breathing or lying down, shortness of breath, fever, chills, sweating, or low blood pressure.
An HIM professional is asked to pull records for patients diagnosed with conditions that have any of the following etiologies
- Infection from group A nonhemolytic streptococcal bacteria following septic thrombophlebitis
- Open heart surgery for prosthetic valves
- Pulmonary infection
- Bone infection
- Skin infection
Which condition are these patients diagnosed with?
Explanation
This condition is an infection of the inner lining of the heart chambers and valves, which can be caused by various microorganisms that enter the bloodstream from different sources. The etiologies listed above are all potential risk factors for developing endocarditis.
Which factor contributes to thrombus formation?
Explanation
A thrombus is a blood clot that forms inside a blood vessel or the heart, which can obstruct blood flow and cause complications such as ischemia or embolism. One of the factors that predispose thrombus formation is stasis of blood flow, which means slow or stagnant movement of blood in a vessel or chamber, which can allow platelets and fibrin to accumulate and form a clot.
A patient presents with fatigue, fever, and night sweats. An echocardiogram showed vegetation.
Which disease is described?
Explanation
This condition is an infection of the inner lining of the heart chambers and valves, which can cause vegetation to form on the valve surfaces. Vegetations are masses of microorganisms, inflammatory cells, and fibrin that adhere to the valve leaflets and can interfere with their function. The symptoms of endocarditis may include fatigue, fever, night sweats, chills, weight loss, or heart murmur.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 52 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Nursingprepexams’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now

