Introduction
Introduction ( 10 Questions)
A nurse is caring for a client who had an emergency cesarean delivery due to fetal distress.
The nurse notices that the client has a large amount of bright red blood on her perineal pad.
What is the nurse’s priority action?
assessing the client’s vital signs and level of consciousness is not a priority action.
These are important indicators of blood loss and shock, but they do not address the source of bleeding. The nurse should first try to stop the bleeding by massaging the fundus and then assess the client’s status.
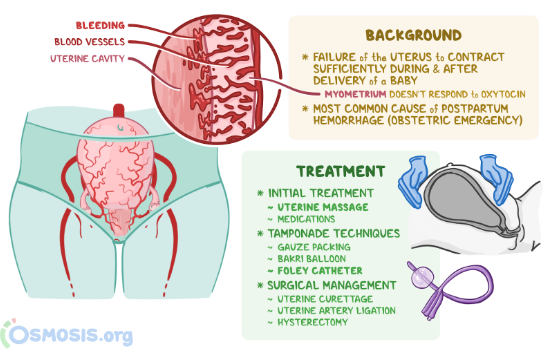
Massage the client’s fundus and check for firmness. This is because the most common cause of postpartum hemorrhage is uterine atony, which is a lack of contraction of the uterus after delivery. Massaging the fundus stimulates the uterus to contract and reduces bleeding from the placental site. Checking for firmness ensures that the uterus is not distended by blood clots or retained placental fragments, which can also cause hemorrhage.
notifying the provider and preparing for a blood transfusion are not priority actions.
These are interventions that may be needed if the bleeding does not stop with fundal massage or if the client develops signs of severe hemorrhage or shock. However, they are not the first steps to take in managing postpartum hemorrhage.
administering oxytocin as prescribed to stimulate uterine contractions is not a priority action. Oxytocin is a uterotonic medication that can help prevent and treat postpartum hemorrhage by causing sustained uterine contractions.
However, it is not the first intervention to try in case of bleeding. The nurse should first massage the fundus and check for firmness, and then administer oxytocin if ordered by the provider.
The correct answer is choice B. Massage the client’s fundus and check for firmness. This is because the most common cause of postpartum hemorrhage is uterine atony, which is a lack of contraction of the uterus after delivery. Massaging the fundus stimulates the uterus to contract and reduces bleeding from the placental site. Checking for firmness ensures that the uterus is not distended by blood clots or retained placental fragments, which can also cause hemorrhage.
Choice A is wrong because assessing the client’s vital signs and level of consciousness is not a priority action.
These are important indicators of blood loss and shock, but they do not address the source of bleeding. The nurse should first try to stop the bleeding by massaging the fundus and then assess the client’s status.
Choice C is wrong because notifying the provider and preparing for a blood transfusion are not priority actions.
These are interventions that may be needed if the bleeding does not stop with fundal massage or if the client develops signs of severe hemorrhage or shock. However, they are not the first steps to take in managing postpartum hemorrhage.
Choice D is wrong because administering oxytocin as prescribed to stimulate uterine contractions is not a priority action. Oxytocin is a uterotonic medication that can help prevent and treat postpartum hemorrhage by causing sustained uterine contractions.
However, it is not the first intervention to try in case of bleeding. The nurse should first massage the fundus and check for firmness, and then administer oxytocin if ordered by the provider.
Normal ranges for blood loss after delivery are less than 500 mL for vaginal birth and less than 1000 mL for cesarean birth. Normal ranges for vital signs and level of consciousness vary depending on the individual client, but some signs of hypovolemia and shock include tachycardia, hypotension, tachypnea, pallor, cold clammy skin, oliguria, anxiety, confusion, and loss of consciousness. Normal range for uterine firmness is a well-contracted uterus that feels like a hard ball at or below the umbilicus.