ATI PN Fundamentals 2020 with NGN Updated 2024
ATI PN Fundamentals 2020 with NGN Updated 2024 ( 41 Questions)
A nurse is reviewing the laboratory results for a client who reports vomiting and diarrhea for 2 days.
Which of the following laboratory findings should the nurse expect?
Choice A is wrong because hypermagnesemia means high magnesium levels in the blood.
Magnesium is another electrolyte that helps with nerve and muscle function, as well as blood pressure and blood sugar regulation.
Hypermagnesemia is rare and usually caused by kidney failure or excessive use of magnesium supplements or laxatives.
Normal magnesium levels are between 1.46 to 2.68 milligram/deciliter.
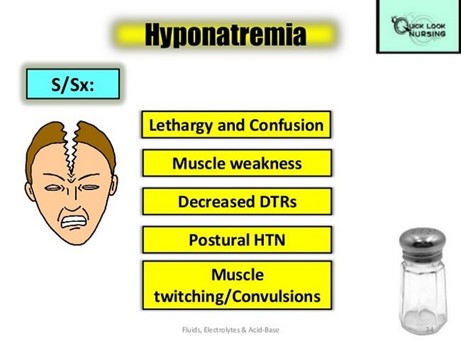
This means low sodium levels in the blood.
Sodium is an electrolyte that helps regulate fluid balance and nerve and muscle function.
Vomiting and diarrhea can cause dehydration and loss of sodium through fluids.
Normal sodium levels are between 135 to 145 millimole/Liter.
Choice C is wrong because hypocalcemia means low calcium levels in the blood.
Calcium is an electrolyte that helps with bone health, muscle contraction, blood clotting and nerve signaling.
Hypocalcemia can be caused by vitamin D deficiency, kidney disease, thyroid problems or certain medications.
Normal calcium levels are between 8.8 to 10.7 milligram/deciliter.
Choice D is wrong because hyperkalemia means high potassium levels in the blood.
Potassium is an electrolyte that helps with nerve and muscle function, especially the heart.
Hyperkalemia can be caused by kidney disease, diabetes, adrenal gland disorders or certain medications.
Normal potassium levels are between 3.6 to 5.5 millimole/Liter.
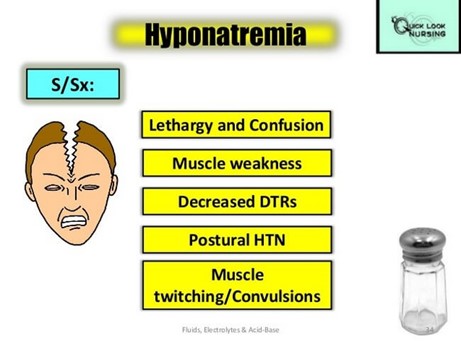
This means low sodium levels in the blood.
Sodium is an electrolyte that helps regulate fluid balance and nerve and muscle function.
Vomiting and diarrhea can cause dehydration and loss of sodium through fluids.
Normal sodium levels are between 135 to 145 millimole/Liter.
Choice A is wrong because hypermagnesemia means high magnesium levels in the blood.
Magnesium is another electrolyte that helps with nerve and muscle function, as well as blood pressure and blood sugar regulation.
Hypermagnesemia is rare and usually caused by kidney failure or excessive use of magnesium supplements or laxatives.
Normal magnesium levels are between 1.46 to 2.68 milligram/deciliter.
Choice C is wrong because hypocalcemia means low calcium levels in the blood.
Calcium is an electrolyte that helps with bone health, muscle contraction, blood clotting and nerve signaling.
Hypocalcemia can be caused by vitamin D deficiency, kidney disease, thyroid problems or certain medications.
Normal calcium levels are between 8.8 to 10.7 milligram/deciliter.
Choice D is wrong because hyperkalemia means high potassium levels in the blood.
Potassium is an electrolyte that helps with nerve and muscle function, especially the heart.
Hyperkalemia can be caused by kidney disease, diabetes, adrenal gland disorders or certain medications.
Normal potassium levels are between 3.6 to 5.5 millimole/Liter.
